Laser welding is mainly aimed at improving the welding efficiency and quality of thin wall materials and precision parts. Today we are not going to talk about the advantages of laser welding but focus on how to use shielding gases for laser welding properly.
Why use shield gas for laser welding?
In laser welding, shield gas will affect the weld forming, weld quality, weld depth, and weld width. In most cases, blowing the assisted gas will have a positive effect on the weld, but it may also bring adverse effects.
When you blow shield gas correctly, it will help you:
✦ Effectively protect the weld pool to reduce or even avoid oxidation
✦ Effectively reduce the splash produced in the welding process
✦ Effectively reduce weld pores
✦ Assist the weld pool spread evenly when solidification, so that the weld seam comes with a clean and smooth edge
✦ The shielding effect of the metal vapor plume or plasma cloud on the laser is effectively reduced, and the effective utilization rate of the laser is increased.
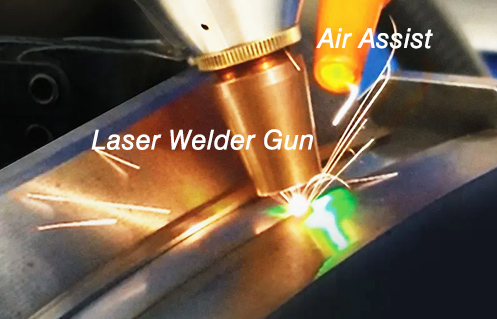
As long as the shield gas type, gas flow rate, and blowing mode selection are correct, you can get the ideal effect of welding. However, incorrect use of protective gas can also adversely affect welding. Using the wrong type of shield gas may lead to creaks in the weld or reduce the mechanical properties of the welding. Too high or too low a gas flowing rate may lead to more serious weld oxidation and serious external interference of the metal material inside the weld pool, resulting in weld collapse or uneven forming.
Types of shield gas
The commonly used protective gases of laser welding are mainly N2, Ar, and He. Their physical and chemical properties are different, so their effects on welds are also different.
Nitrogen (N2)
The ionization energy of N2 is moderate, higher than that of Ar, and lower than that of He. Under the radiation of the laser, the ionization degree of N2 stays on an even keel, which can better reduce the formation of a plasma cloud and increase the effective utilization rate of the laser. Nitrogen can react with aluminum alloy and carbon steel at a certain temperature to produce nitrides, which will improve weld brittleness and reduce toughness, and have a great adverse impact on the mechanical properties of weld joints. Therefore, it is not recommended to use nitrogen when welding aluminum alloy and carbon steel.
However, the chemical reaction between nitrogen and stainless steel generated by nitrogen can improve the strength of the weld joint, which will be beneficial to improve the mechanical properties of the weld, so the welding of stainless steel can use nitrogen as a shielding gas.
Argon (Ar)
The ionization energy of Argon is relatively low, and its ionization degree of it will become higher under the action of a laser. Then, Argon, as a shielding gas, cannot effectively control the formation of plasma clouds, which will reduce the effective utilization rate of laser welding. The question arises: is argon a bad candidate for welding use as a shielding gas? The answer is No. Being an inert gas, Argon is difficult to react with the majority of metals, and Ar is cheap to use. In addition, the density of Ar is large, it will be conducive to sinking to the surface of the weld molten pool and can better protect the weld pool, so Argon can be used as conventional protective gas.
Helium (He)
Unlike Argon, Helium has relatively high ionization energy that can control the formation of plasma clouds easily. At the same time, Helium does not react with any metals. It’s truly a good choice for laser welding. The only problem is that Helium is relatively expensive. For fabricators that provide mass-production metal products, helium will add a huge amount to the cost of production. Thus helium is generally used in scientific research or products with very high added value.
How to blow the shield gas?
First of all, it should be clear that the so-called "oxidation" of the weld is only a common name, which theoretically refers to the chemical reaction between the weld and the harmful components in the air, leading to the deterioration of the weld. Commonly, the weld metal reacts with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen in the air at a certain temperature.
To prevent the weld from being "oxidized" requires reducing or avoiding contact between such harmful components and the weld metal under high temperature, which is not only in the molten pool metal but the whole period from the time when the weld metal is melted until the molten pool metal is solidified and its temperature is cooling down to a certain temperature.
Two main ways of blowing shield gas
▶ One is blowing shield gas on the side axis, as shown in Figure 1.
▶ The other is a coaxial blowing method, as shown in Figure 2.
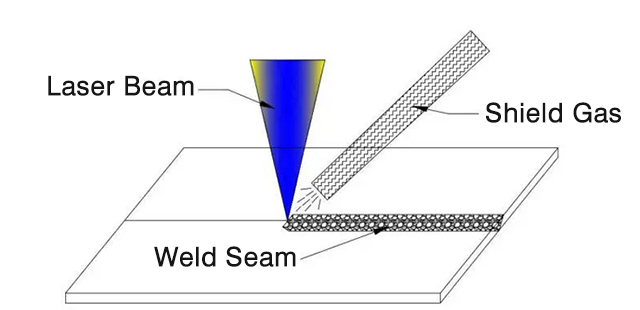
Figure 1.
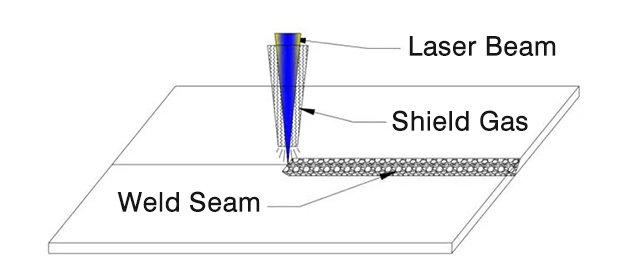
Figure 2.
The specific choice of the two blowing methods is a comprehensive consideration of many aspects. In general, it is recommended to adopt the way of the side-blowing protective gas.
Some examples of laser welding
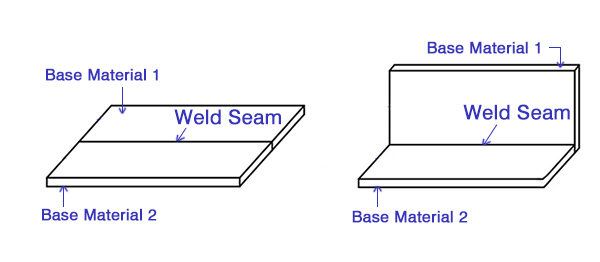
1. Straight bead/line welding
As shown in Figure 3, the weld shape of the product is linear, and the joint form can be a butt joint, lap joint, negative corner joint, or overlapped welding joint. For this type of product, it is better to adopt the side-axis blowing protective gas as shown in Figure 1.
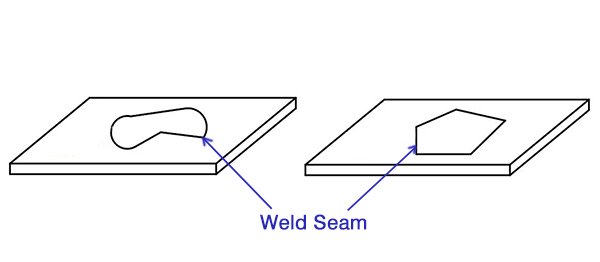
2. Close figure or area welding
As shown in Figure 4, the weld shape of the product is a closed pattern such as plane circumference, plane multilateral shape, plane multi-segment linear shape, etc. The joint form can be butt joint, lap joint, overlapping welding, etc. It is better to adopt the coaxial protective gas method as shown in Figure 2 for this type of product.
The selection of protective gas directly affects the welding quality, efficiency, and cost of production, but because of the diversity of welding material, in the actual welding process, the selection of welding gas is more complex and needs comprehensive consideration of welding material, welding method, welding position, as well as the requirements of the welding effect. Through the welding tests, you can choose the more suitable welding gas to achieve better results.
Interested in laser welding and willing to learn how to choose shield gas
Related Links:
Post time: Oct-10-2022

