What is laser welding? Laser Welding Explained! All you need to know about Laser Welding, including key principle and main process parameters!
Many customers don’t understand the basic working principles of laser welding machine, let alone choosing the right laser welding machine, however Mimowork Laser is here to help you make the right decision and provide additional support to aid you in understanding laser welding.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is a type of melting welding, using the laser beam as a welding heat source, the welding principle is that a specific method to stimulate the active medium, forming resonant cavity oscillation, and then transform into the stimulated radiation beam, when the beam and the work piece contact each other, the energy is absorbed by the work piece, when the temperature reaches the melting point of the material can be welded.
According to the principal mechanism of welding pool, laser welding has two basic welding mechanisms: heat conduction welding and deep penetration (keyhole) welding. The heat generated by heat conduction welding is diffused to the work piece through heat transfer, so that the weld surface is melted, no vaporization should be happening, which is often used in the welding of low-speed thin-ish components. Deep fusion welding vaporizes the material and forms a large amount of plasma. Due to elevated heat, there will be holes in the front of the molten pool. Deep penetration welding is the most widely used laser welding mode, it can weld the work piece thoroughly, and the input energy is huge, leading to fast welding speed.
Process Parameters in Laser Welding
There are many process parameters that affect the quality of laser welding, such as power density, laser pulse waveform, defocusing, welding speed and the choice of auxiliary shielding gas.
Laser Power Density
Power density is one of the most important parameters in laser processing. With a higher power density, the surface layer can be heated to boiling point within a microsecond, resulting in a large amount of vaporization. Therefore, the high-power density is advantageous for material removal processes such as drilling, cutting and engraving. For low power density, it takes several milliseconds for the surface temperature to reach the boiling point, and before the surface vaporizes, the bottom reaches the melting point, which is easy to form a good melting weld. Therefore, in the form of heat conduction laser welding, the power density range is 104-106W/cm2.

Laser Pulse Waveform
Laser pulse waveform is not only an important parameter to distinguish material removal from material melting, but also a key parameter to determine the volume and cost of processing equipment. When the high intensity laser beam is shot to the surface of the material, the surface of the material will have 60 ~ 90% of the laser energy reflected and considered loss, especially gold, silver, copper, aluminum, titanium and other materials that have strong reflection and fast heat transfer. The reflectance of a metal varies with time during a laser pulse. When the surface temperature of the material rises to the melting point, the reflectance decreases rapidly, and when the surface is in the melting state, the reflectance stabilizes at a certain value.
Laser Pulse Width
Pulse width is an important parameter of pulsed laser welding. The pulse width was determined by the depth of penetration and the heat affected zone. The longer the pulse width was, the larger the heat affected zone was, and the depth of penetration increased with the 1/2 power of the pulse width. However, the increase of pulse width will reduce the peak power, so the increase of pulse width is generally used for heat conduction welding, resulting in a wide and shallow weld size, especially suitable for lap welding of thin and thick plates. However, lower peak power results in excess heat input, and each material has an optimal pulse width that maximizes the depth of penetration.
Defocus Quantity
Laser welding usually requires a certain amount of defocusing, because the power density of the spot center at the laser focus is too high, which is easy to evaporate the welding material into holes. The distribution of power density is relatively uniform in each plane away from the laser focus.
There are two defocus modes:
Positive and negative defocus. If the focal plane is located above the workpiece, it is positive defocus; otherwise, it is negative defocus. According to geometric optics theory, when the distance between the positive and negative defocusing planes and the welding plane is equal, the power density on the corresponding plane is approximately the same, but in fact, the obtained molten pool shape is different. In the case of negative defocus, greater penetration can be obtained, which is related to the formation process of molten pool.

Welding Speed
Welding speed determines welding surface quality, penetration depth, heat affected zone and so on. The welding speed will affect the heat input per unit time. If the welding speed is too slow, the heat input is too high, resulting in the workpiece burning through. If the welding speed is too fast, the heat input is too little, resulting in the workpiece welding partially and unfinished. Reducing welding speed is usually used to improve the penetration.
Auxiliary Blow Protection Gas
Auxiliary blow protection gas is an essential procedure in high power laser welding. On the one hand, to prevent metal materials from sputtering and contaminating the focusing mirror; On the other hand, it is to prevent the plasma generated in the welding process from focusing too much and prevent the laser from reaching the surface of the material. In the process of laser welding, helium, argon, nitrogen and other gases are often used to protect the molten pool, so as to prevent the workpiece from oxidation in the welding engineering. Factors such as the type of protective gas, the size of air flow and the blowing Angle have a great impact on the welding results, and different blowing methods will also have a certain impact on the welding quality.
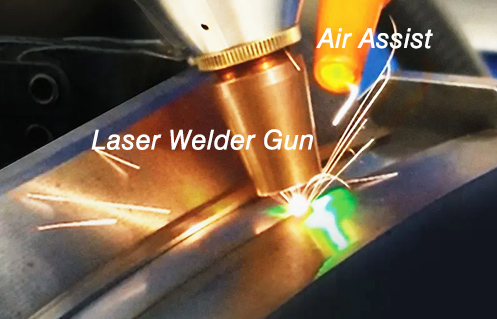
Our recommended Handheld Laser Welder:

Laser Welder - Working Environment
◾ Temperature range of working environment: 15~35 ℃
◾ Humidity range of working environment: < 70%No condensation
◾ Cooling: water chiller is necessary due to the function of heat removing for laser heat-dissipating components, ensuring the laser welder runs well.
(Detailed use and guide about water chiller, you can check the: Freeze-proofing Measures for CO2 Laser System)
Wanna Know more about Laser Welders?
Post time: Dec-22-2022




